
To understand if the exchange rates are at the correct levels, you need to rely on indices like the cost of living index. You must note that the Big Mac Index is just a simplification of the purchasing power parity theory. Such trades will stay possible till the exchange rate doesn’t adjust to the correct level. But wait, how much money is a Big Mac in India? That’s right, ₹100! So, by just exporting the same Big Mac to the UK, you ended up with enough money for 4 Big Macs! When you convert this back to Indian rupees, you will get ₹400. So, hypothetically, if you bought a Big Mac worth ₹100 from India and sold it in the UK, you would get £200. But, a Big Mac worth ₹100 in India would be worth £200 in the UK. Why should the exchange rate be at the level suggested by the Big Mac Index? It would mean that the US dollar is overvalued compared to the euro. But, suppose the exchange rate is actually at $1 = €3. So, according to the Big Mac Index, the exchange rate for euros to dollars should be $1 = €1.5. Similarly, suppose if in the Euro Area the Big Mac costs €150, and it costs $100 in the USA. It would mean that the Indian rupee is undervalued compared to the British pound. But, suppose the exchange rate shows that ₹1 = £0.5. So, according to the Big Mac Index, the Indian rupee’s exchange rate against the British pound should be ₹1 = £2. Suppose in India the Big Mac costs ₹100 and it costs £200 in the UK. Let’s look at a couple of exchange rate calculation examples that use the Big Mac Index. In that case, theoretically, the exchange rate is not at the correct level. Suppose the ratio of Big Mac prices in 2 countries is not equal to the exchange rate between 2 countries. By comparing the prices of Big Macs across countries, we are comparing the prices of almost identical baskets of goods and services across countries.Īlso Read: What Is The Difference Between Nifty and Sensex? How to understand the Big Mac Index? If this is not the case, it would mean that the current exchange rate is not at the correct level.īig Macs are sold worldwide and made with more or less the same ingredients and other inputs like labour, equipment, etc.
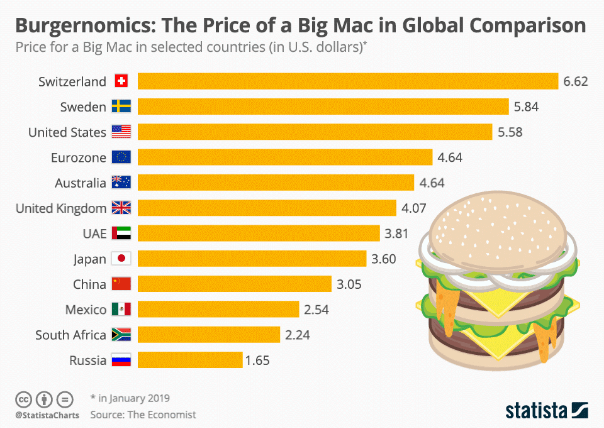

Why did The Economist spend so much time and money comparing burger prices?Īccording to purchasing power parity (PPP) theory, in the long run, the prices of an identical basket of goods and services should be equal in any 2 countries. The Big Mac Index compares the price of Big Macs, a burger offered by McDonald’s, across several countries. This article explores the meaning of the Big Mac Index, the theory it attempts to explain, and other such off-beat indices. In 1986, The Economist developed the Big Mac Index to simplify purchasing power parity theory. Purchasing power parity, a theory that attempts to explain exchange rates, is one such theory. Various economic theories can be very difficult for laypeople to understand.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
